Construction Work Zone Safety
IoT-enabled Work Zone Proximity Warning System

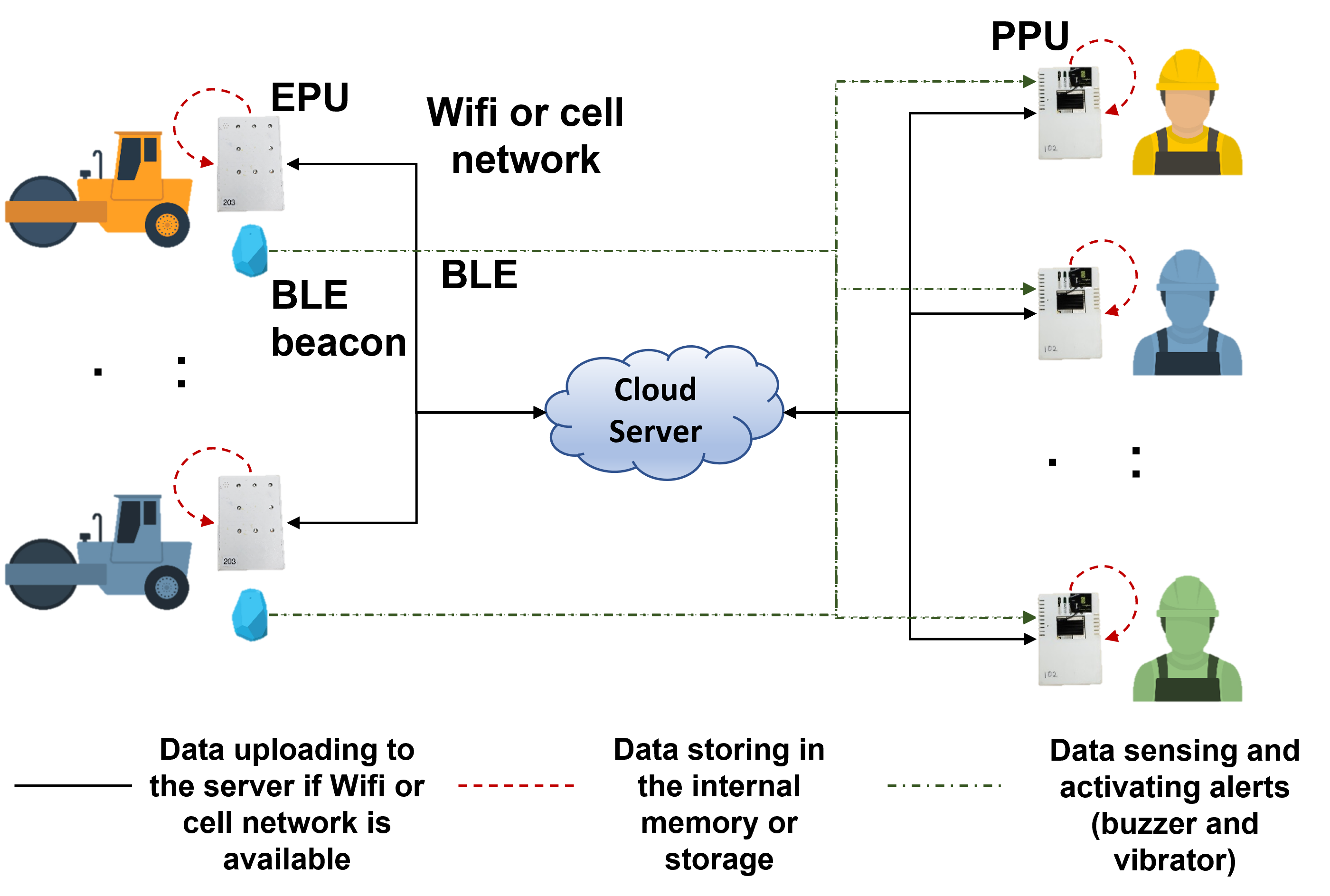
This research proposes an Internet of Things (IoT)-driven proximity warning system that provides an alert to workers whenever they are close to heavy equipment. Also, five case studies were conducted to practically validate the system in actual construction sites. The system includes equipment protection units (EPUs), personal protection units (PPUs), and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons. By calculating the distance between PPUs and BLE beacons based on the signal strength, EPUs and PPUs provide auditory and vibration alerts to equipment operators and workers when they are in an alert range. Through five case studies, the system achieved a precision, recall, and f1-score of 89.21%. 97.45%, and 0.931, respectively. From the perspective of workers, the alerts provided to workers were clearly recognized because 91% of workers answered in the questionnaire survey that they were able to recognize the alerts in time. In addition, practical lessons learned were derived from the case studies so that the system can be implemented with the expected performance. Based on the findings of this study, it is expected that the IoT-based proximity warning system can be a practical solution to proximity hazards in actual construction sites.
Projects
- Phase III: Smart Proximity Work Zone Safety Technology Deployment funded by Georgia Department of Transportation
- A Smart IoT Proximity Alert System for Highway Work Zone Safety funded by NCHRP IDEA program
- AwareSite- Smart and Connected Construction Jobsite for Construction Safety and Productivity Improvement funded by Dysruptek
Image-based Proximity Avoidance System using Augmented Reality in Wearable Device
 This research proposes a vision-based hazard avoidance system that proactively informs workers of potentially dangerous situations. The system enables workers to recognize and consequently avoid dangers before accidents occur by displaying augmented hazard information on a wearable device. The system comprises of three modules; a vision-based site monitoring module that utilizes image capture device and wearable devices to identify site hazards, a safety assessment module that uses captured image data and fuzzy-based reasoning to evaluate the safety level of each object, and a visualization module that provides actionable information such as hazard orientation, distance, and safety level. The safety information provided by the proposed system can mitigate hazards and improve construction site safety.
This research proposes a vision-based hazard avoidance system that proactively informs workers of potentially dangerous situations. The system enables workers to recognize and consequently avoid dangers before accidents occur by displaying augmented hazard information on a wearable device. The system comprises of three modules; a vision-based site monitoring module that utilizes image capture device and wearable devices to identify site hazards, a safety assessment module that uses captured image data and fuzzy-based reasoning to evaluate the safety level of each object, and a visualization module that provides actionable information such as hazard orientation, distance, and safety level. The safety information provided by the proposed system can mitigate hazards and improve construction site safety.
Projects
- Intelligent Interactive InfoEcosystem for Automating and Optimizing On-site Safety/Construction, funded by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
Construction Worker’s Behavior and Productivity Monitoring
Evaluation of the effective locations and quantify of motion sensors
 This research evaluated the effectiveness of motion sensors’ numbers and locations to maximize motion recognition performance of machine learning algorithms. The evaluation is conducted by generating different datasets containing motion sensor data collected from the sensors located on different body parts. Comparing the performance of five machine learning models trained using the datasets, the desired numbers and locations of motion sensors are identified. The quasi-experimental test with multiple subjects is conducted to validate the findings of the evaluation.
This research evaluated the effectiveness of motion sensors’ numbers and locations to maximize motion recognition performance of machine learning algorithms. The evaluation is conducted by generating different datasets containing motion sensor data collected from the sensors located on different body parts. Comparing the performance of five machine learning models trained using the datasets, the desired numbers and locations of motion sensors are identified. The quasi-experimental test with multiple subjects is conducted to validate the findings of the evaluation.
Automated recognition of worker’s motions using LSTM networks
 This research proposes Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks for recognizing construction workers’ motions. The LSTM networks were validated through case studies in one bridge construction site and two road pavement sites. The LSTM networks showed classification accuracies of 97.6%, 95.93%, and 97.36% from three different field test sites, respectively. Through the case studies, the technical and practical feasibility of the LSTM networks was properly investigated. With the LSTM networks, it is expected that the individual workers’ behavior and working conditions can be automatically monitored and managed without excessive manual observation.
This research proposes Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks for recognizing construction workers’ motions. The LSTM networks were validated through case studies in one bridge construction site and two road pavement sites. The LSTM networks showed classification accuracies of 97.6%, 95.93%, and 97.36% from three different field test sites, respectively. Through the case studies, the technical and practical feasibility of the LSTM networks was properly investigated. With the LSTM networks, it is expected that the individual workers’ behavior and working conditions can be automatically monitored and managed without excessive manual observation.
Projects
- PFI-TT: Smart Pose and Position Guidance System for Construction Worker’s Safety and Productivity funded by National Science Foundation (NSF)
Real-time Crane Operation Visualization
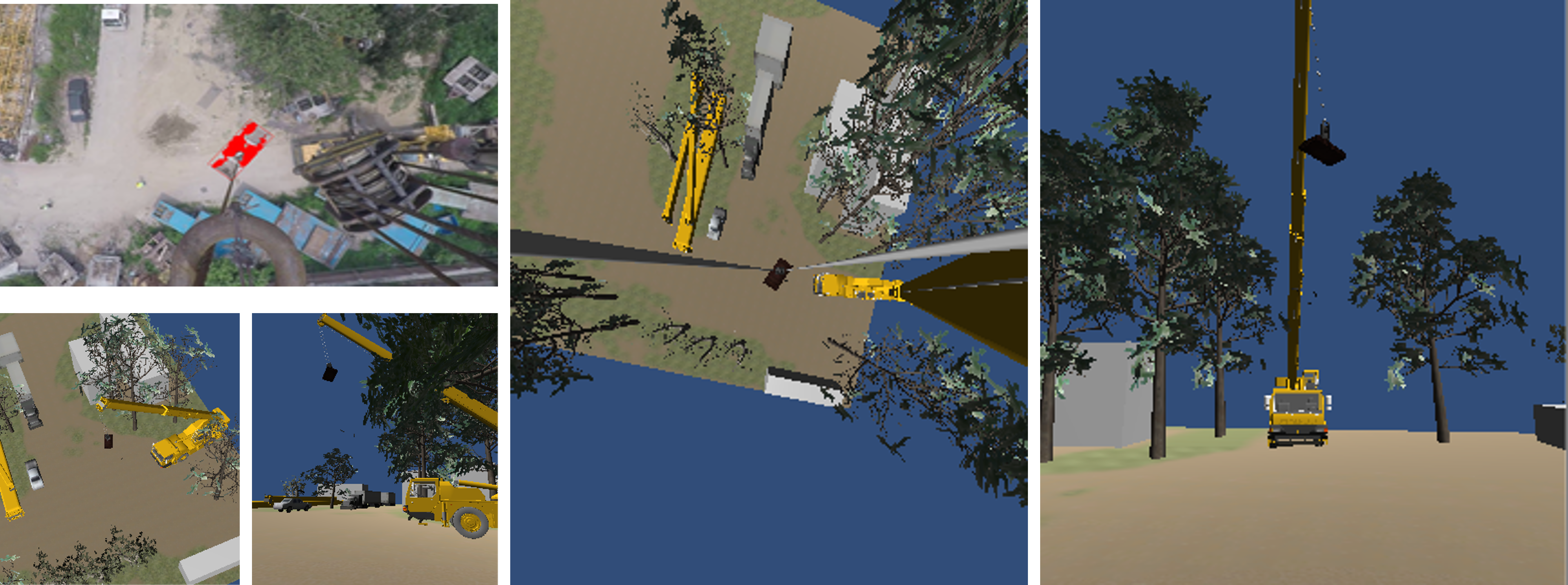 This research aims to visualize the load sway of the crane using top-view images and Unity3D software for improving operator’s spatial awareness in blind lifts. A series of tests in a lab environment and real-world scenarios were conducted to evaluate the proposed approach. The results from the tests indicated that the proposed framework and methods were able to monitor and visualize the crane states in real-time and thus provide the operator with adequate assistance to identify and mitigate unsafe conditions during blind lifts.
This research aims to visualize the load sway of the crane using top-view images and Unity3D software for improving operator’s spatial awareness in blind lifts. A series of tests in a lab environment and real-world scenarios were conducted to evaluate the proposed approach. The results from the tests indicated that the proposed framework and methods were able to monitor and visualize the crane states in real-time and thus provide the operator with adequate assistance to identify and mitigate unsafe conditions during blind lifts.
Projects
- Advanced Blind Lift Safety using Crane Motion Sensors and Real-time Visualization funded by Chevron Energy Technology Company
